
What Types of Filling Materials Are Available?
Several dental filling materials are available in the field of dentistry. Teeth can be filled with gold; porcelain; silver amalgam which consists of mercury mixed with silver, tin, zinc, and copper, Composites resin fillings or tooth-colored, plastic and glass materials.. The location and extent of the decay, cost of filling material, dentist’s recommendation assist in determining the type of filling that will best address your needs.
Cast gold
Advantages:
- Strength – can withstand chewing forces
- Durabilit – can last to 10 years or more and doesn’t corrode
- Aesthetics – Some patients preferred gold rather than silver amalgam
Disadvantages:
- Cost – more than other materials, up to 10 times higher than cost of amalgam filings
- Additional visits – requires at least 2 visits to do it
- Galvanic shoc – a gold filling placed immediately next to the silver, amalgam filling can cause a sharp pain. (a reactions between the metals and saliva causes electric current to oocur but the case is rarerly)
- Aesthetics – most patients find composites filings more pleasing to the eye
Amalgam fillings
Advantages:
- Durability – last 15 years compare to composites filling
- Cost – is less expensive than composite fillings
- Strength – can withstand chewing forces
Disadvantages:
- Discoloration – amalgam filling can create grayish color to the surrounding tooth structure
- Poor esthetics – fillings don’t match the color of your natural teeth
- Destruction of more tooth structure – cut the healthy parts of the tooth –often removed to make space large enough to hold the amalgam fillings
- Cracks and fractures – although all teeth expand and contract in the presence of hot and cold liquids, which ultimately can cause the tooth to crack or fracture, amalgam material – in comparison with other filling materials–may experience a wider degree of expansion and contraction and lead to a higher incidence of cracks and fractures
Tooth-colored composite fillings
Advantages:
- Aesthetics – the color of the composites can be closely matched to the color of existing teeth; is particularly well suited for use in front teeth or visible parts of teeth
- Versatility in uses – in addition to use as a filling material for decay, composite fillings can also be used to repair chipped, broken or worn teeth
- Bonding to tooth structure – composite fillings actually chemically bond to tooth structure, providing further support to the tooth
- Tooth – sparing preparation- less tooth structure needs to be removed compared with amalgams when removing decay and preparing for the filling
Disadvantages:
- Cost– more expensive than amalgam fillings
- Chipping – depending on location, composites materials can chip off the tooth
- Increased chair time – Due to the process when to apply the composite materials, these fillings can take up to 30 minutes longer than amalgams
- Lack of durability – composite fillings wear out sooner than amalgam
*Tooth-colored, composite resin fillings, two types of tooth-colored fillings exist
- Ceramics and
- Glass ionomer.
- Ceramics, are made most often of porcelain, are more resistant to staining than composite resin material but are also more abrasive. This material generally lasts more than 15 years and more expensive than gold.
- Glass Ionomer – is made of acrylic and a specific type of glass material. This material is most commonly used for fillings below gum line and for fillings in young children( drilling is still required). Glass Ionomer generally last 5 years or less with cost comparable to composite resin.
What Types of Filling Materials Are Available?
Several dental filling materials are available in the field of dentistry . Teeth can be filled with gold; porcelain; silver amalgam which consists of mercury mixed with silver, tin, zinc, and copper, Composites resin fillings or tooth-colored, plastic and glass materials.. The location and extent of the decay, cost of filling material, dentist’s recommendation assist in determining the type of filling that will best address your needs.
What Are Indirect Fillings?
Indirect fillings are similar to composite or tooth-colored fillings except that they are made in a dental laboratory and require two visits before being placed. Indirect fillings are considered when not enough tooth structure remains to support a filling but the tooth is not so severely damaged that is needs a crown.
There are two types of indirect fillings – inlays and onlays.
- Inlays are similar to fillings but the entire work lies within the cusps on the chewing surface of the tooth.
- Onlays are more extensive than inlays, covering one or more cusps. Onlays are sometimes called partial crowns. Inlays and onlays are more durable and last much longer than traditional fillings – up to 30 years. They can be made of tooth-colored composite resin, porcelain or gold. Inlays and onlays weaken the tooth structure, but do so to a much lower extent than traditional fillings.
Another type of inlay and onlay – direct inlays and onlays – follow the same processes and procedures as the indirect, the difference is that direct inlays and onlays are made in the dental office and can be placed in one visit. The type of inlay or onlay used depends on how much sound tooth structure remains and consideration of any cosmetic concerns.
What’s a Temporary Filling and Why Would I Need One?
Temporary fillings are used under the following circumstances:
- For fillings that require more than one appointment – for example, before placement of gold fillings and for certain filling procedures (called indirect fillings) that use composite materials.
- To allow a tooth’s nerve to “settle down” if the pulp became irritated Following a root canal treatment
- For emergency dental treatment I s needed to relief toothache.
Temporary fillings are just that; they are not meant to last. They usually fall out, fracture, or wear out within 1 month. Be sure to contact your dentist to have your temporary filling replaced with a permanent one. If you don’t, your tooth could become infected or you could have other complications.
Are Amalgam-Type Fillings Safe?
Over the past several years, concerns have been raised about silver-colored fillings, otherwise called amalgams. Because amalgams contain the toxic substance mercury, some people think that amalgams are responsible for causing a number of diseases, including autism, Alzheimer’s disease, and multiple sclerosis.
The American Dental Association (ADA), the FDA, and numerous public health agencies say amalgams are safe, and that any link between mercury-based fillings and disease is unfounded. The causes of autism, Alzheimer’s disease, and multiple sclerosis remain unknown. Additionally, there is no solid, scientific evidence to back up the claim that if a person has amalgam fillings removed, he or she will be cured of these or any other diseases.
How Should I Care for My Teeth With Fillings?
To maintain your fillings, you should follow good oral hygiene practices – visiting your dentist regularly for cleanings, brushing with a fluoride-containing toothpaste, and flossing at least once daily. If your dentist suspects that a filling might be cracked or is “leaking” (when the sides of the filling don’t fit tightly against the tooth, this allows debris and saliva to seep down between the filling and the tooth, which can lead to decay). Dentist will take x-ray to assess the situation. If your tooth is extremely sensitive, if you feel a sharp edge, if you notice a crack in the filling, or if a piece of the filling is missing, call your dentist for an appointment.
What Types of Filling Materials Are Available?
Several dental filling materials are available in the field of dentistry . Teeth can be filled with gold; porcelain; silver amalgam which consists of mercury mixed with silver, tin, zinc, and copper, Composites resin fillings or tooth-colored, plastic and glass materials.. The location and extent of the decay, cost of filling material, dentist’s recommendation assist in determining the type of filling that will best address your needs.
Problems With Dental Fillings
Pain and Sensitivity
Tooth sensitivity following placement of a filling is fairly common. A tooth may be sensitive to pressure, air, sweet foods, or temperature. Usually, the sensitivity resolves on its own within a few weeks. During this time, avoid those things that are causing the sensitivity. Pain relievers are generally not required.
Contact your dentist if the sensitivity does not subside within 2 to 4 weeks or if your tooth is extremely sensitive. Dentist may recommend you use a desensitizing toothpaste, may apply a desensitizing agent to the tooth, or possibly suggest a root canal procedure.
Pain around the fillings can also occur. If you experience pain when you bite, the filling is interfering with your bite. You will need to return to your dentist and have the filling reshaped.
If you experience pain when your teeth touch, the pain The pain is likely caused by the touching of two different metal surfaces (for example, the silver amalgam in a newly filled tooth and a gold crown on another tooth with which it touches). This pain should resolve on its own within a short period of time. If the decay was very deep to the pulp of the tooth, you may experience a “toothache-type” pain. This “toothache” response may indicate this tissue is no longer healthy. If this is the case, “root canal” treatment will be required.
Deteriorating Fillings
Constant pressure from grinding , clenching or chewing can cause dental fillings to wear away, chip or crack. Although you may not be able to tell that your filling is wearing down, your dentist can identify weaknesses in your restorations during a regular check-up.
If the filling is large or the recurrent decay is extensive, there may not be enough tooth structure remaining to support a replacement filling. In these cases, your dentist may need to replace the filling with a crown.

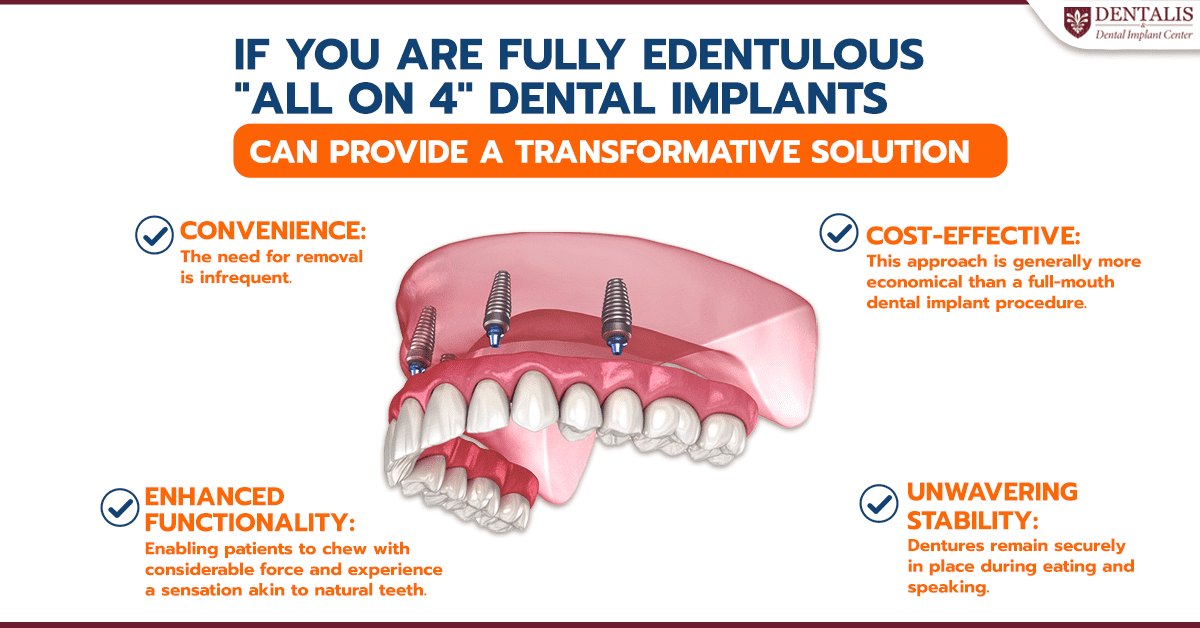
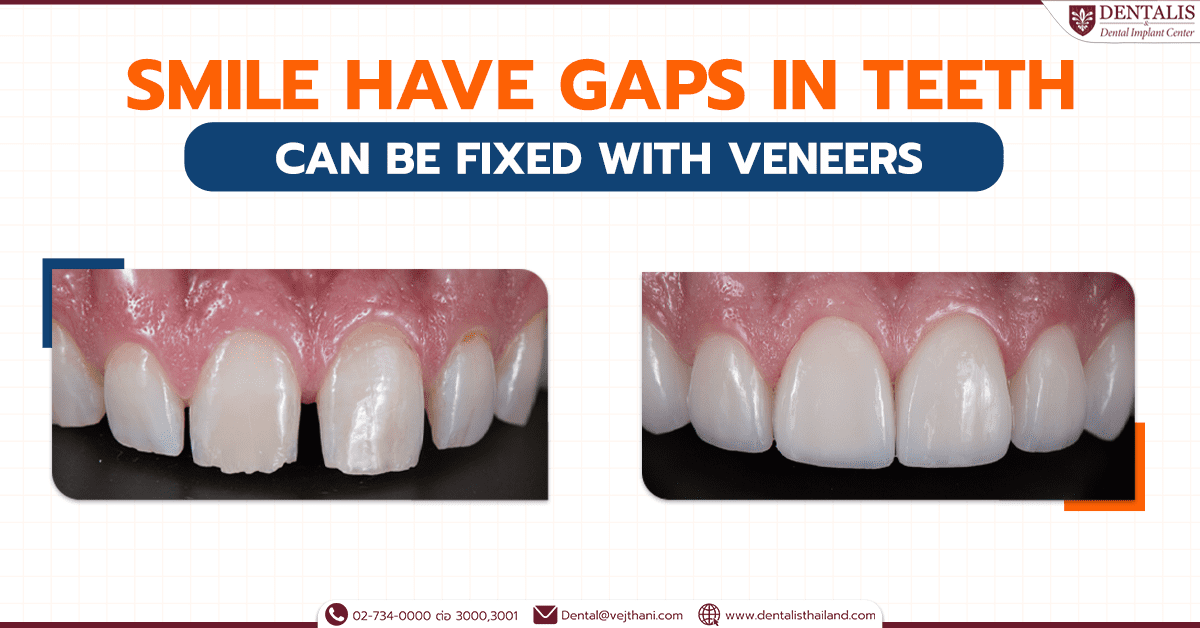
02-734-0000
Dentalis